2021 Graduates! Shitong Wei, Lifeng Wei, Qin Ding
I was blessed to see three of my Ph.D. students graduate, especially so because it was during the Covid-19 pandemic. It was a heroic effort on all of their parts to not get set back during this hard time.
 Qin Ding, Shitong Wei, me, Lifeng Wei (left to right)
Qin Ding, Shitong Wei, me, Lifeng Wei (left to right)
Qin Ding
Thesis: Advances in Stochastic Contextual Bandits
Qin has established herself as an expert in contextual bandits with an ambitious research agenda. She has focused on extending the scope and capabilities of contextual bandit algorithms. This includes robustness, automated hyperparameter tuning, fast stochastic updating, and non-stationarity. You can see work via her google scholar page.
One thing that I think was very nice was her use of bandit-over-bandits to adapt to adversarial attacks. She found that the meta-bandit could be used to tune any number of parameters, and this actually worked very well in practice. This was even true for theoretically derived parameters such as what is used in UCB algorithms! You should not leave home without it.
Shitong Wei
Thesis: Multidimensional Graph Trend Filtering
Shitong has produced a nice body of work on trend filtering for exponential families in multiple dimensions. One application was adaptive small area estimation for Covid-19 case proportion in CA. A common approach to dealing with small counts in epidemiology is to average over large spatial regions. The idea behind her method is that if you have low counts during a time period than you need to have a more coarse spatial resolution. You can do this using spatio-temporal graph trend filtering with the Poisson likelihood over a mobility graph. In the image below you can see the different spatial regions identified during a low count (left) and high count (right) time period.

Lifeng Wei
Thesis: Applications of Statistics in Machine Learning Problems
Lifeng has a dissertation that represents his diverse interests and expertise. Centered around statistics in machine learning, his chapters are:
- Search to Compress: Layer-wise Compression of Deep Neural Networks by Monte Carlo Tree Search
- Unsupervised Object Segmentation with Explicit Localization Module
- A Graph-Based Dataset Similarity Metric
- COVID-19 Prediction Efforts at Health Davis Together
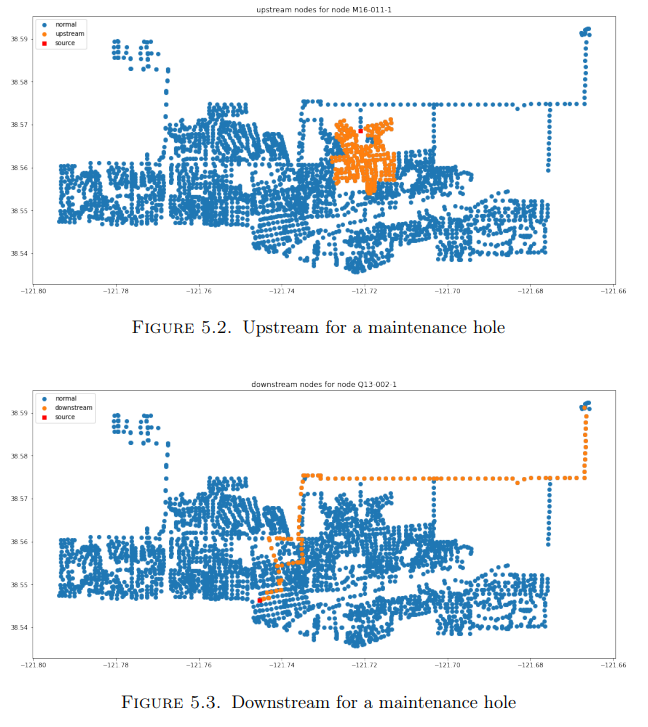
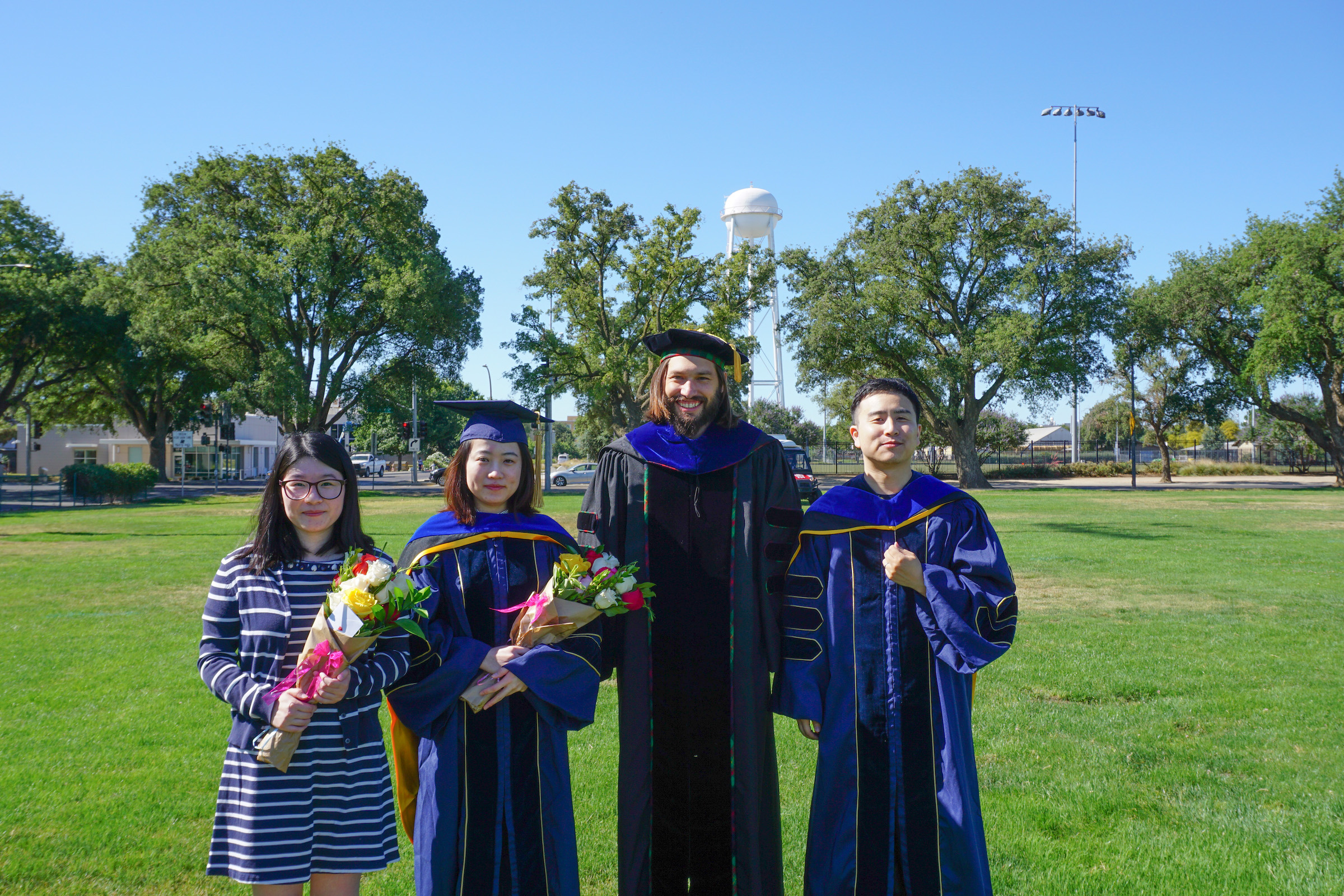
Lifeng’s efforts were critical to the operations of the modeling team in Healthy Davis Together. He worked with the Safegraph mobility data to produce mobility networks that were used to identify commute patterns to and from Davis. One notable contribution was his work on mapping the Covid-19 wastewater sampling data to saliva testing. This was used to validate the wastewater sampling by correlating it with the test positivity within census blocks. He did this by associating nodes in the wastewater network with census blocks. Then all locations upstream of a maintenance hole were used to build the population that is upstream of the sampling location. You can see an example of upstream locations to a sampling site in the image below.